Not clear on the basics of how solar panels work? Looking to purchase solar panels but have no clue about the different types on the market? We have got you covered in the article.
Solar panels have become a popular choice for generating clean, renewable energy, revolutionizing the way we power our homes. Understanding the basics and various types of solar panels is crucial for making informed decisions about the best option that suits your energy needs and budget. In this guide, we’ll delve into the basics of how solar panels work and the different types of solar panels, exploring their unique features, benefits, and technical specifications.
How do solar cells/solar panels work?
Solar cells, also known as photovoltaic cells, are devices that convert light energy into electrical energy through the photovoltaic effect.
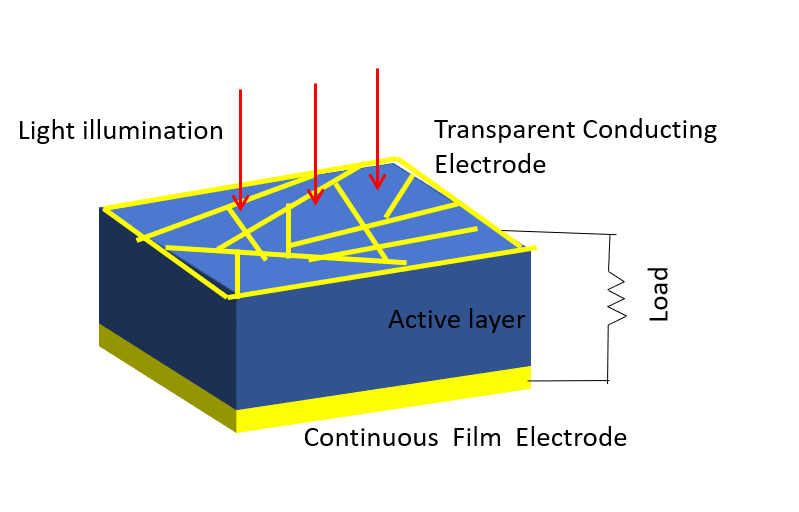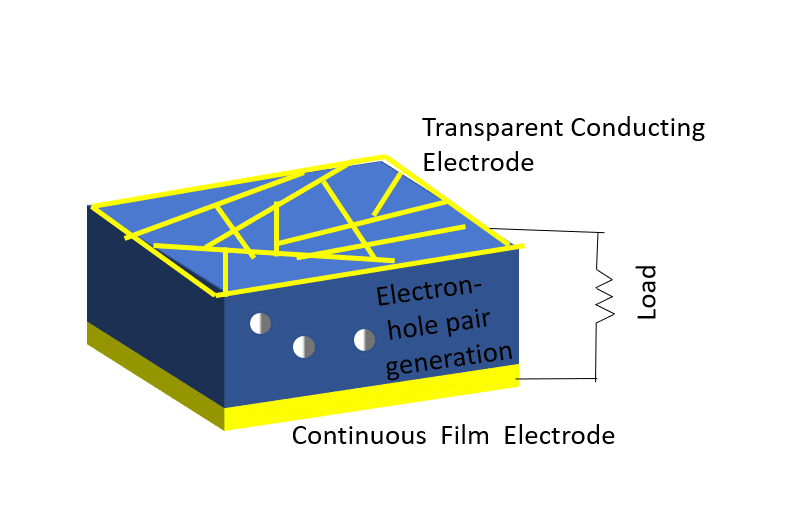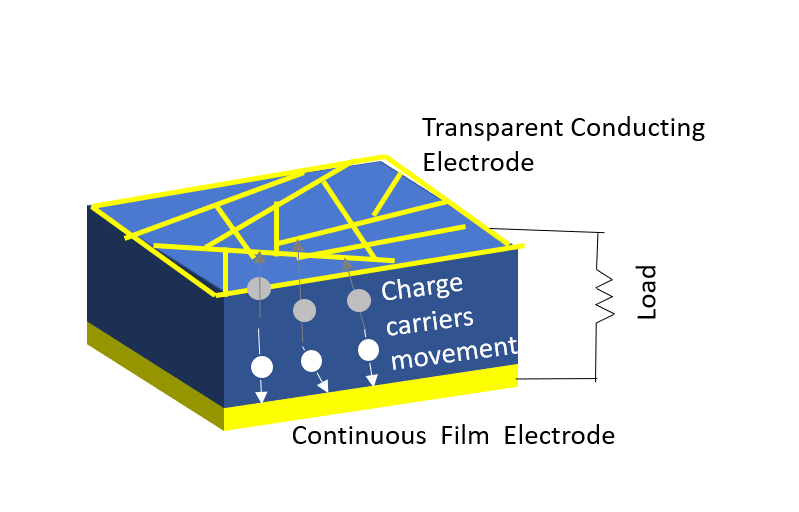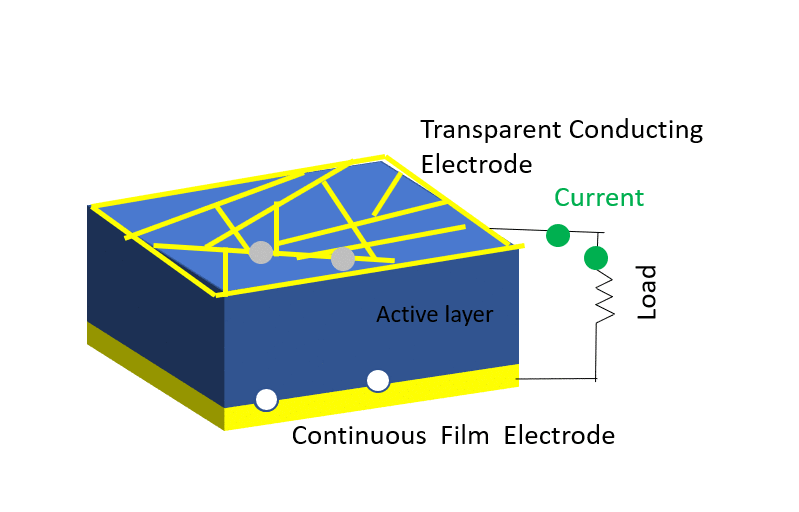
Here’s a simplified explanation of how solar cells work:
- Absorption of Photons: When sunlight, which is composed of tiny particles called photons, strikes the surface of a solar cell, the semiconductor material within the cell absorbs the photons.
- Generation of Electron-Hole Pairs: The absorbed energy from the photons allows some of the electrons in the semiconductor material to break free from their atoms, creating negatively charged particles called electrons and positively charged particles called holes.
- Directional Flow of Electrons: The electric field within the solar cell facilitates the directional movement of the liberated electrons towards the front surface of the cell, creating a flow of electric current.
- Collection of Current: The electric current generated by the flow of electrons is collected by metal contacts on the surface of the solar cell, allowing it to be drawn as usable electric power.
- Conversion to Usable Electricity: Multiple solar cells are interconnected within a solar panel, and the direct current (DC) electricity generated by the panel can be converted into alternating current (AC) electricity using an inverter. This AC electricity can then power various devices and appliances in homes and businesses.
The efficiency of solar cells in converting sunlight into electricity depends on factors such as the type of semiconductor material used, the intensity of the sunlight, the temperature, and the design of the solar cell. With advancements in technology, researchers continue to develop more efficient and cost-effective solar cells to harness the abundant energy from the sun and provide a clean and sustainable energy source for various applications.
What are the most common types of Solar Panels?
Monocrystalline Panels
Monocrystalline solar panels are recognized for their high efficiency and sleek appearance. They are made from single-crystal silicon, giving them a uniform dark color.

These panels perform exceptionally well in low-light conditions, making them an ideal choice for locations with limited sunlight. Their efficiency typically ranges from 15% to 20%, making them one of the most efficient types of solar panels available. While monocrystalline panels can be more expensive than other options, their durability and performance justify the investment for many homeowners.
Polycrystalline Panels
Pros
Cons
- High efficiency, making them ideal for installations with limited space.
- Higher cost compared to other types of solar panels.
- Better performance in low-light conditions compared to other types.
- Vulnerable to high temperatures, which can affect their efficiency.
- Long lifespan, typically lasting over 25 years, with some manufacturers offering warranties of up to 30 years.
- The production process involves high energy consumption and potentially higher carbon footprint.
Polycrystalline Panels
Polycrystalline solar panels are another popular option known for their cost-effectiveness and versatility. These panels are made from multiple silicon fragments melted together, giving them a characteristic blue hue.

While they are slightly less efficient than monocrystalline panels, with an efficiency range of 13% to 16%, they are more affordable and offer a practical solution for those looking to install a solar energy system on a budget. Polycrystalline panels are durable, easy to install, and have a long lifespan, making them a reliable choice for many solar energy applications.
Polycrystalline Panels
Pros
Cons
- Lower production costs compared to monocrystalline panels, making them a more budget-friendly option.
- Slightly lower efficiency compared to monocrystalline panels, resulting in a larger installation area for the same energy output.
- Good efficiency rates, making them suitable for residential and commercial installations.
- Lower space efficiency, which might not be suitable for installations with limited rooftop space.
- Durable and long-lasting, requiring minimal maintenance over their lifespan.
- Reduced performance in high temperatures can affect their overall energy production.
Thin-Film Panels
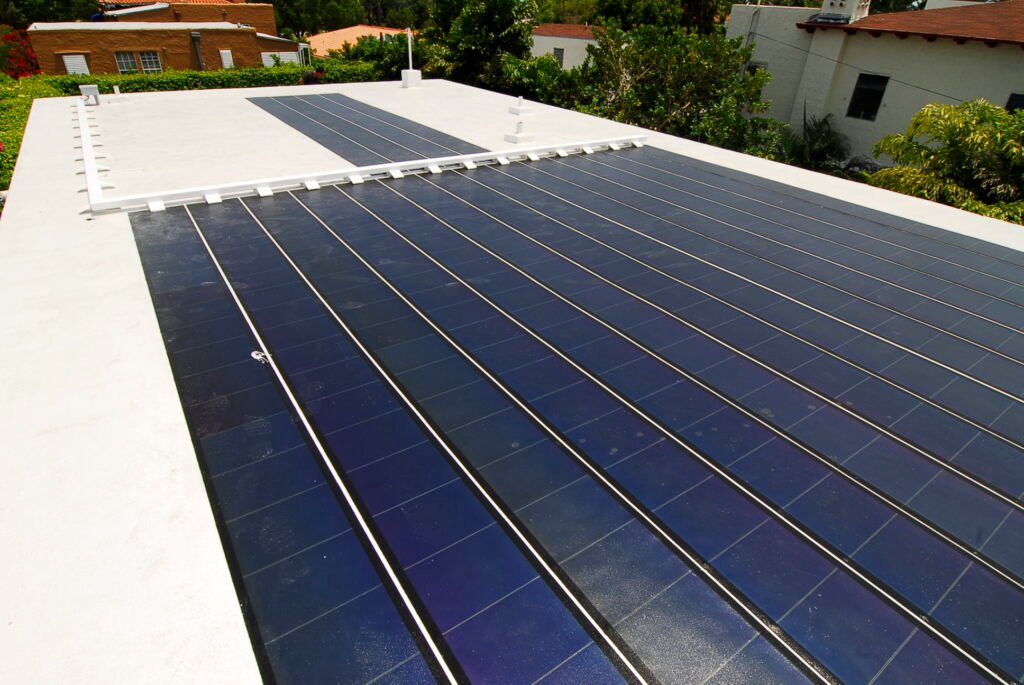

Thin-film solar panels are known for their lightweight and flexible design, allowing them to be used in various applications that traditional solar panels cannot accommodate. They are made by depositing thin layers of photovoltaic material onto a substrate, such as glass, plastic, or metal. While thin-film solar panels are less efficient compared to crystalline silicon panels, with an efficiency range of 7% to 13%, they are more cost-effective to produce and offer better performance in high-temperature environments. Additionally, their flexibility makes them suitable for curved surfaces and portable solar applications.
Thin-Film Panels
Pros
Cons
- Cost-effective production process, leading to lower overall panel costs.
- Lower efficiency compared to crystalline silicon panels, requiring larger installation areas for the same energy output.
- Versatile applications, including curved surfaces and portable solar devices.
- Shorter lifespan compared to crystalline silicon panels, typically lasting around 10-15 years.
- Better performance in high temperatures compared to crystalline silicon panels.
- Vulnerability to degradation over time, leading to a gradual decrease in energy production.
Bifacial Solar Panels
Bifacial solar panels have gained popularity for their unique design, which allows them to capture sunlight from both sides of the panel. These panels can generate additional electricity by utilizing reflected and scattered light, making them more efficient than traditional one-sided solar panels.
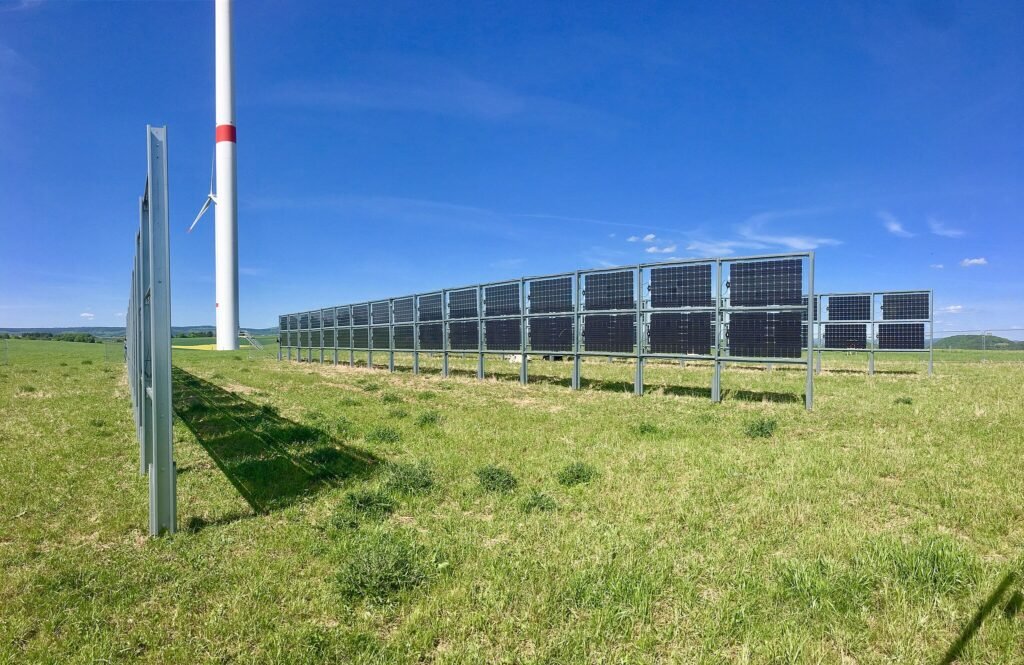

Bifacial panels are available in both monocrystalline and polycrystalline forms, offering a high level of versatility to suit different energy needs. While they are relatively more expensive than traditional solar panels, their increased energy production and efficiency often justify the additional investment, especially in environments with high albedo surfaces or light-reflective backgrounds.
Bifacial Solar Panels
Pros
Cons
- Higher energy output due to their ability to capture sunlight from both sides, increasing overall efficiency.
- Higher upfront costs compared to traditional solar panels, impacting the initial investment.
- Installation versatility allows for ground-mounted and rooftop installations.
- The need for specific installation conditions to optimize their two-sided capabilities, potentially limiting their applicability in certain environments.
- Potential for better performance in locations with high albedo, such as snowy environments.
- The possibility of increased soiling on the rear side, requiring regular cleaning for optimal performance.
PERC Solar Cells
PERC stands for Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell. This advanced type of photovoltaic cells that has gained prominence in the solar industry for their increased energy efficiency and improved performance under various conditions.
As the solar industry continues to evolve, PERC solar cells represent a significant advancement in solar cell technology mainly because it allows us to harness solar energy in a more efficient and reliable way. With their enhanced energy conversion capabilities and improved performance in various environmental conditions, PERC solar cells contribute to the continued growth and adoption of solar power as a clean and sustainable energy source.
PERC Solar Cells
Pros
Cons
- Higher efficiency compared to traditional solar panels, leading to increased energy output.
- Slightly higher manufacturing costs compared to traditional solar panels, impacting initial investment.
- Better performance in high temperatures, making them suitable for installations in hot climates.
- Potential degradation over time, requiring proper maintenance and monitoring for optimal performance.
- Improved overall energy production, even under low-light conditions.
- Susceptibility to potential light-induced degradation can affect their long-term efficiency.
Concentrated Photovoltaic (CPV) Solar Panels
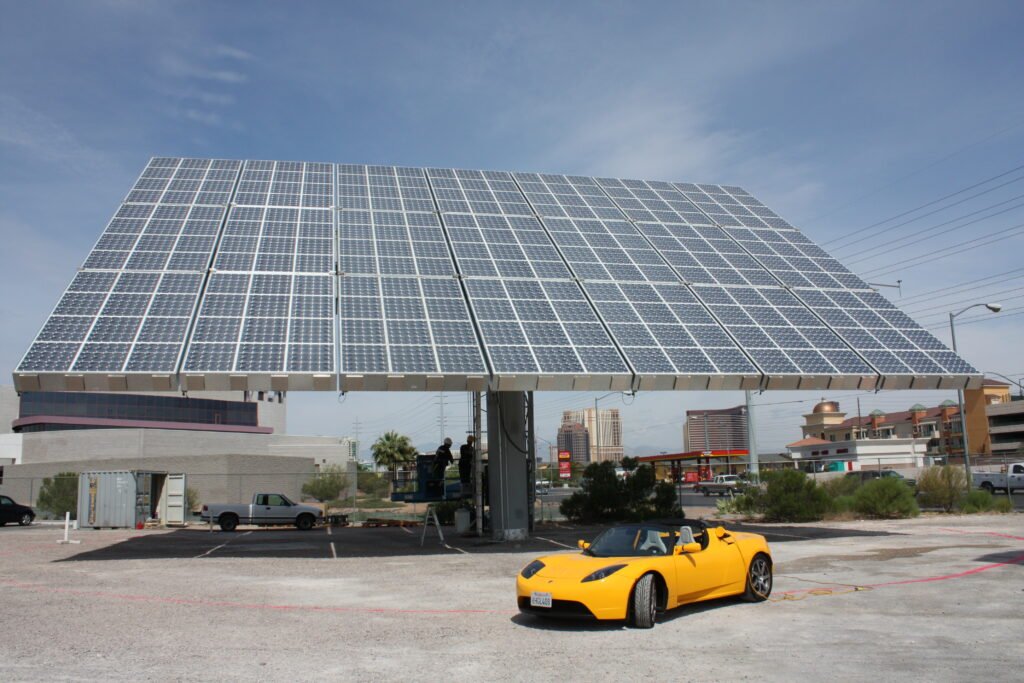

Concentrated photovoltaic (CPV) solar panels are a specialized type of solar technology that uses lenses or mirrors to focus sunlight onto small, highly efficient solar cells. The concentrated light significantly increases the efficiency of the solar cells, allowing CPV systems to achieve higher energy production compared to traditional solar panels. In fact, CPV systems are most effective in regions with high direct sunlight, making them suitable for use in solar power plants and large-scale solar energy projects. While CPV technology offers impressive efficiency levels, it is typically more complex and expensive to install, requiring careful consideration of the specific environmental conditions and energy requirements before implementation.
BIPV Solar Panels
Pros
Cons
- Potential to achieve higher efficiencies compared to traditional photovoltaic systems
- More complex: systems require precise tracking systems to follow the sun’s movement
- The use of smaller, high-efficiency solar cells in CPV systems can lead to reduced material costs
- Rely on direct sunlight and are less effective in diffuse light conditions
- Requires less space compared to traditional solar panels (More electricity produced per unit area)
- Increased maintenance requirements and costs compared to traditional solar panels
- Typically perform better in high-temperature environments
- Limited Geographic Suitability, best suited for regions with high direct normal irradiance
Building-Integrated Photovoltaics (BIPV)
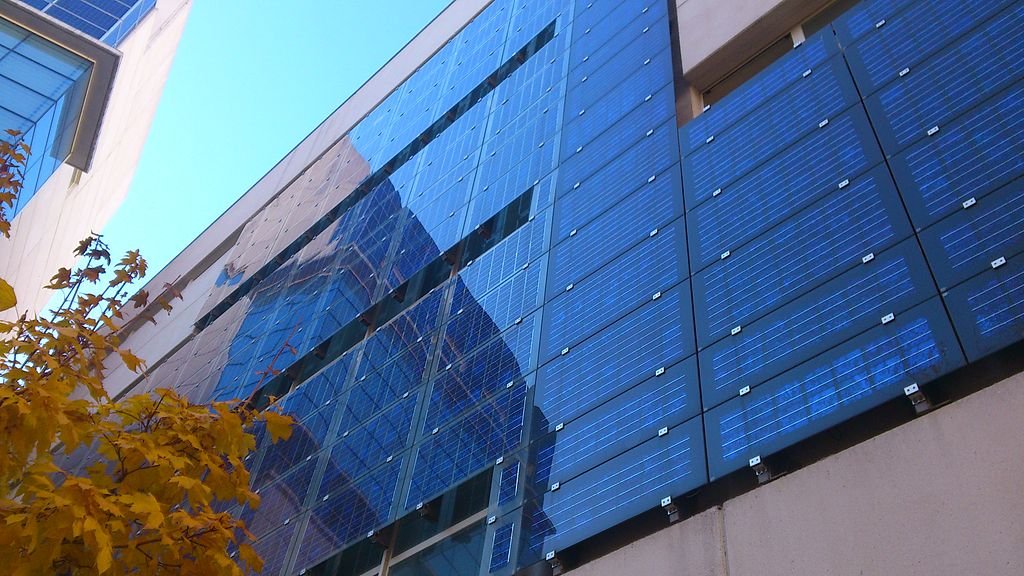

Building-integrated photovoltaics (BIPV) seamlessly integrate solar panels into the architecture of buildings and structures. These panels can serve as functional building materials, such as roof tiles, shingles, or facades, while simultaneously generating electricity. In addition, BIPV systems offer a visually appealing and sustainable solution for incorporating solar energy into the design and construction of residential and commercial buildings. While BIPV technology may have slightly lower efficiency compared to traditional solar panels, its ability to blend in with the overall building design and reduce the overall construction costs make it an attractive option for eco-friendly and aesthetically conscious construction projects.
BIPV Solar Panels
Pros
Cons
- Seamlessly integrated into the building’s design, providing a visually appealing and streamlined appearance.
- Tend to be more expensive than traditional solar panels and standard building materials
- Better space efficiency, serving a dual purpose, acting as both a building material and an electricity generator
- Requires specialized installation techniques and expertise
- Increase in value due to their energy-efficient and sustainable features, appealing to environmentally conscious buyers.
- May have slightly lower energy conversion efficiency compared to traditional solar panels
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the different types of solar panels is essential for selecting the most suitable option for your specific energy needs and budget. Whether you prioritize high efficiency, cost-effectiveness, versatility, or seamless integration into building structures, there is a solar panel type that can meet your requirements. By considering factors such as efficiency, cost, durability, and specific environmental conditions, you can make an informed decision that maximizes the benefits of solar energy for your home or business.
If you have any further questions or need assistance in choosing the right solar panel type, leave a comment below. Or, you can also reach out to our Reddit community to help you harness the power of the sun and embrace a more sustainable and eco-friendly energy solution.





Leave a Reply